Artificial intelligence that predicts heart attacks in use in hospitals
A revolutionary artificial intelligence (AI) technology which predicts a person’s risk of having a deadly heart attack and how soon they might have one is now available in the UK.
Called CaRi-Heart, the AI takes a standard coronary CT scan, and extracts more information than even the most well-trained doctors are able to see.
Built by Oxford-based company Caristo Diagnostics, the system detects signs of inflammation in the walls of the organ’s own arteries which supply it with blood and oxygen.
This ability is beyond the scope of standard CT scans, which look solely for blockages and plaque aggregation.
It is designed as an “early warning system” to identify when a person’s heart is perhaps showing signs of damage, but the arteries have yet to develop any hazardous obstructions.
“All of the inflammation is there, but we have never been able to access it before Caristo and CaRi-Heart”, Dr Ronak Rajani, a consultant cardiologist at the Harley Street Clinic and Professor of Cardiovascular Imaging at King's College London, told The Telegraph.
He, alongside Professor John Deanfield, was instrumental in bringing the technology into Britain's hospitals and it is now available at the Harley Street Clinic for £495. Talks are also underway for it to be available, for free, on the NHS.
Around half of heart attacks do not occur in fully-blocked arteries
For patients, the act of getting the scan is no different, but the results are sent off to Oxford, analysed by Caristo, and returned within a handful of days.
The difference between a regulation coronary CT scan and the new analysis lies in what comes after the scan itself, when the images are inputted into CaRi-Heart.
Scientists say that although plaque build up is a serious problem, around half of all heart attacks do not occur in fully-blocked arteries.
The other half are caused when small pieces of plaque rupture, releasing cholesterol into the blood which triggers a clot and ultimately leads to a heart attack. These are impossible to predict with current CT scans.
But what Dr Cheerag Shirodaria, the co-founder and CEO of Caristo, realised, is that these impromptu clots occur in areas of the heart where the artery walls are inflamed.
He identified that inflammation led to tiny areas of discoloration in the heart tissue, and built an AI model capable of quantifying these changes.
Cardiologists can now spot issues ahead of time
The manifestation of this plan is a new metric, called the Fat Attenuation Index (FAI), which allows cardiologists to identify parts of the heart’s blood supply where things are suboptimal.
The importance of the technology, the researchers say, is that it allows, for the first time, doctors to diagnose heart health issues before artery obstruction occurs. It opens up an earlier window in which to identify high-risk people and subsequently intervene in order to lower the likelihood of them having a fatal heart attack.
It was tested by the British Heart Foundation which involved 4,000 patients who had a CT scan, and gave their permission for their results, and follow-up data, to be used by Caristo.
The nine-year project found people with an abnormal FAI were up to nine times more likely to die of a heart attack in the next nine years than those with normal FAI readings.
It also revealed that one third of patients who get a low-risk diagnosis from a standard scan are actually at much higher risk when studied by CaRi-Heart.
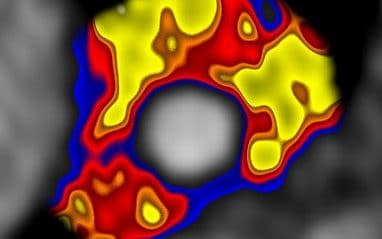
Each of the heart’s three arteries — left anterior descending, left circumflex and right coronary — are given their own FAI score. The lower, the better.
These are then compared to the rest of the population and a patient is given a percentile for how they measure up. The 50th percentile is the average, and being ranked higher indicates higher risk of a heart attack.
The system also produces a “CaRi-Risk” figure which tells the patient the likelihood of them having a fatal cardiac event in the next eight years.
If this figure is alarmingly high, doctors intervene with either medication, such as aspirin or statins, to alleviate some of the inflammation, or lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, cutting out alcohol, and being more active.
Standard CT scans show white lines on a black background, but CaRi-Heart throws up a cacophony of colours revealing various levels of inflammation, reflective of their FAI grade.
Yellow is good, and indicates the walls of the arteries are calm. The more red and blue appears, the more distressed the vessel is.
Professor Deanfield called the technique revolutionary and a “one-stop-shop investigation”.
Dr Shirodaria told The Telegraph: “If we are really going to get a handle on coronary heart disease, which is still the biggest killer, we need to focus much more on prevention. All of our effort is spent when people have disease and it is already established.
“If we can identify earlier when we can modify the risk then ultimately that translates into significant cost savings for the NHS but also, more importantly, significant lives saved.”
‘I’m off for a run, and to bin all the processed food in my fridge’
The scan was exactly the same as a normal CT scan, writes Joe Pinkstone. My pulse and blood pressure were taken, I was asked to lie down in front of an enormous doughnut and a team of very personable experts explained the procedure to me.
A small cannula in the arm allowed a radiographer to insert some biological dye into my veins (which produced a warm sensation akin to a toasty blanket, or the unfortunate sensation of having wet oneself), and I was asked to hold my breath for ten seconds.
I was then inserted into the centre of the machine, now humming gently as enormous magnets, weighing as much as four Mini Coopers — started to spin.
The CaRi-Heart results came back less than 48 hours later. Dr Ranjnani and Dr Shirodaria walked me through my results a day later.
Based solely on the old-school CT scan, Dr Rajani described my heart arteries as “beautiful and smooth”, “pristine” and “absolutely normal”. Zero plaque, nowhere to be seen. Good news.
But then Dr Cheerag Shirodaria revealed what CaRi-Heart found and said two of my three coronary arteries are in good shape and on par for what would be expected for a healthy 25-year-old man.
Yet, the same could not be said for the right coronary artery, which provides oxygen to one half of my body’s blood pump. “It is showing signs of inflammation,” was the verdict.
Dr Shirodaria was, as doctors so deftly do, lightening the blow. My artery is in fact in the 91st percentile for people of my age. It was, as the experts said, an early warning sign.
My absolute risk of a fatal heart attack is low, just 0.9 per cent in the next eight years, but my relative risk compared to my peers, is high. But I would have never known this before CaRi-Heart, with the CT scan likely only providing a false sense of security.
Lifestyle changes — fewer takeaways, more exercise, less alcohol — was the advice. No need for statins yet, but, if things don’t improve, that could be my fate in a decade or two.
But with the foresight afforded by CaRi-Heart, I can now make changes to improve the odds. The results were surprisingly moving, a quick and easy scan showed signs I need to address my health, and gave me enough warning to implement changes.
Tech like this will save thousands of lives, but the true impact of it will not be felt for decades, when people who find signs of inflammation change their fate and as a result avoid a fatal heart attack. Well worth the money, and I’m off for a run and to bin all the processed food in my fridge.

